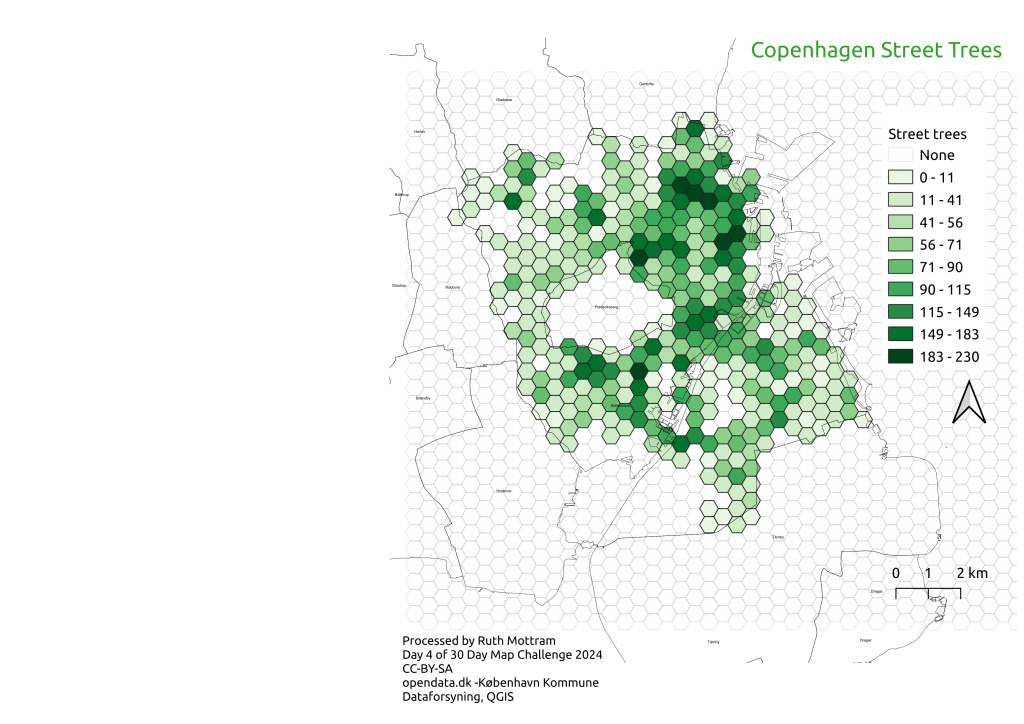
Yesterday in 30 Day Map Challenge I rather hurriedly made a map showing the density of street trees in Copenhagen shown as hexagons. However, there is a big gap in the overall map, because the dataset I used only covered Copenhagen Kommune (local authority) area and Frederiksberg is a separate local authority area where I could not find the data. This was, to put it mildly a little irritating.
A fellow mastodon user (@tlohde) suggested using the outputs from openstreetmap to fill out the gaps. (And even helpfully provided some code to do so, which should tell you a lot about why I like mastodon so much). A very hurried 10 minutes reprocessing gives the revised map on the below, which has happily filled in much of the Frederiksberg gap. However, a closer comparison with the previous version above shows that, it’s not nearly the same…
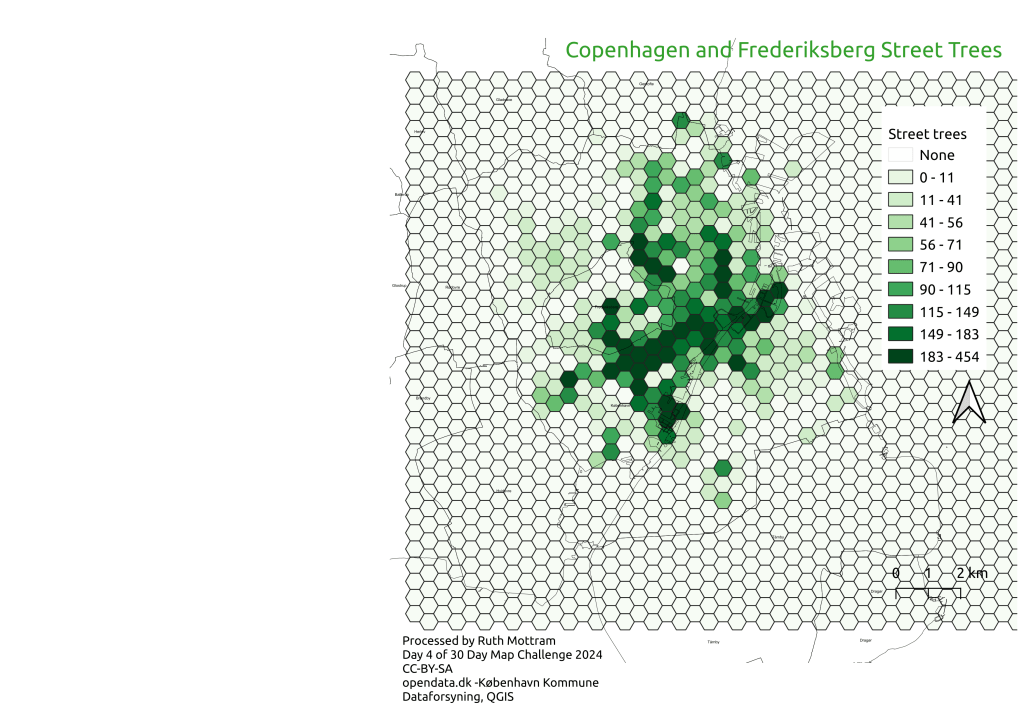
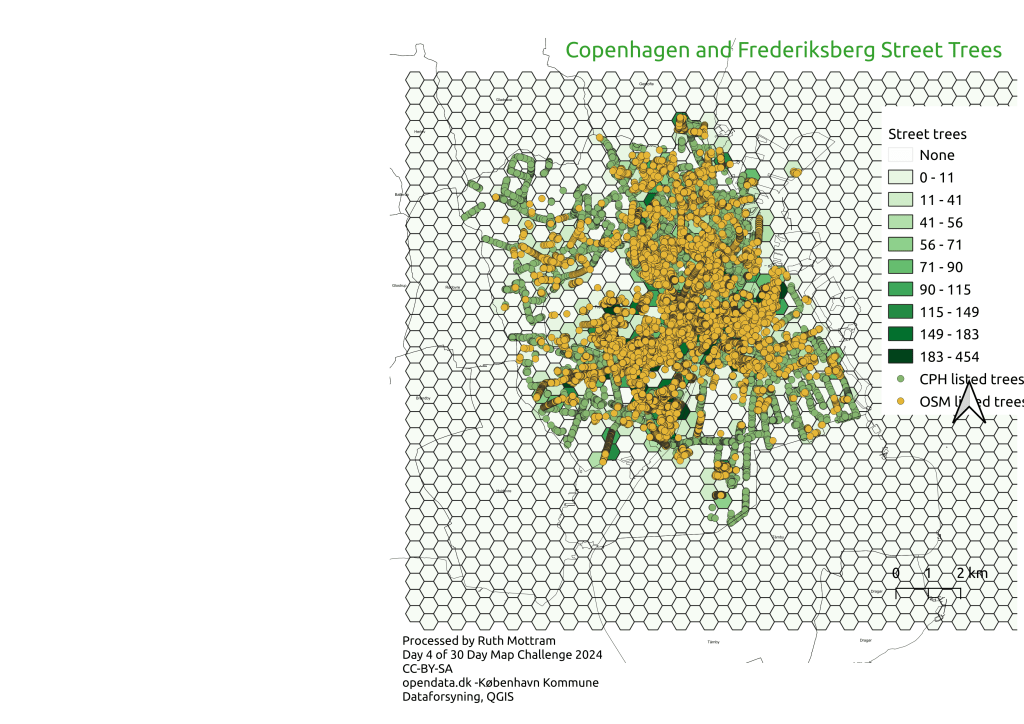
The first thing to note is that the maximum number of trees in a polygon from the OSM data is 454, almost twice the 230 from the Copenhagen city council data set. The second thing is that I’m unsure exactly what time periods the Copenhagen data is from. It’s possible there has been a wholesale planting since the original data was collected, but there is no date on the opendata.dk page to indicate when it was sampled, so I can’t know how up to date it is. Openstreetmap may also be missing data of course (and a small remaining gap in northern Frederiksberg suggests it might be). However, the whole central axis of the plot has changed too.
I overlaid the individual trees on the map plot, the two are quite similar, and the long lines suggest tat plantings are following major roads in the city. I wonder however if the main difference is one of definition. Perhaps street trees from the Copenhagen kommune dataset does not include parks and of course those on private property, compared to those in OSM?
Does it really matter? Well maybe. Street trees provide a valuable service in communities: they shade the streets in hot summer days (and can lead to substantial cooling). They also soak up rainwater and their flowers and fruit feed city ecosystems, quite apart from their aesthetic properties. How to protect, conserve and expand the numbers if we don’t know where they are? Or are not for that matter?
I don’t really have time to dig down into this mystery further. 30 Day Map challenge is really about the tools but either way it’s a lesson. No matter how clever the tool, if the underlying data is missing, wrong or otherwise biased in someway, the map will also be wrong.
I’m tempted to add, that all maps are wrong, but some of them are useful..


